Calculations
 Algebra System (G.A.S.)
Algebra System (G.A.S.) provides many predefined operations, functions and constants.
provides many predefined operations, functions and constants.
- geometric functions
- arithmetic operations
- arithmetic functions
- differentiate
- integrated
- trigonometric functions
- more functions
- logic operators
- logic functions
- constants
Geometric functions require  -objects as inputs. Simply specify the name of the object. Objects whith names containing indices have to be written using _.
-objects as inputs. Simply specify the name of the object. Objects whith names containing indices have to be written using _.
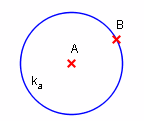
E.g. the label of the circle above was input as k_a, but is displayed as ka.
- x-component
- y-component
- distance of two points
- length of a segment
- radius of a circle
- Measuring angles in degrees
- Measuring angles in the radian measure
- parallel-function
- orthogonal-funktion
Input
- X(point)
 . X returns the value of the x-coordinate of the point.
. X returns the value of the x-coordinate of the point.
Example
- X(A) with A(2.23;1.3) returns 2.23
Input
- Y(point)
 . Y returns the value of the y-coordinate of the point.
. Y returns the value of the y-coordinate of the point.
Example
- Y(A) with A(2.23;1.3) returns 1.3
Input
- Dist(point1,point2)
 -points point1 and point2 is calculated with Dist.
-points point1 and point2 is calculated with Dist.
Example
- Dist(A,B) with A(1;0) and B(0;1) returns 1.414...
Input
- L(segment)
 . L returns the length of the segment. If segment is a line, a ray or a vector then L returns the distance of the two defining points.
. L returns the length of the segment. If segment is a line, a ray or a vector then L returns the distance of the two defining points.
Example
- L(a) with a defined by A(1;0) and B(0;1) returns 1.414...
Input
- R(circle)
 . R returns the length of the radius. Indices have to be written with _ (see example).
. R returns the length of the radius. Indices have to be written with _ (see example).
Example
- R(k_a) returns the radius of k_a
Input
- Deg(punkt1,punkt2,punkt3)
Example
- Deg(A,B,C) with A(1;0), B(0;1) and C(1;1) returns 45.0
Measuring angles in radian measure
Input
- Rad(point1,point2,point3)
Example
- Rad(A,B,C) with A(1;0), B(0;1) and C(1;1) returns 0.785...
Input
- Par(line1,line2)
Example
- Par(a,b) with a || b returns True
Input
- Ortho(line1,line2)
Example
- Ortho(a,b) with a || b returns False
Input
- argument1 + argument2
Input
- argument1 - argument2
Input
- argument1 * argument2
Input
- argument1 / argument2
(natural) exponential function
Input
- Exp(argument)
- Exp(x)
- Exp(X(A))
Input
- Log(argument)
- Log(x)
- Log(X(A))
- Log(E^2) returns 2
Inputs
- Pow(base, exponent)
- base^exponent
- Pow(3, x) means 3^x
- x^2
- Y(C)^2
Input
- Sqrt(argument)
- Sqrt(x)
- Sqrt(Y(B))
Input
- D(expression, variable)
- D(expression, {variable, n})
- D(expression, variable)/.variable->value
- D(expression, {variable, n})/.variable->value
Examples
- D(Sin(x),x) returns Cos(x)
- D(Sin(x),{x,2}) returns -Sin(x)
- D(Sin(x),x)/.x->Pi/2 returns 0
- D(Sin(x),{x,2})/.x->Pi/2 returns -1
Input
- Int(expression, variable)
- Int(expression, variable)/.variable->value
Examples
- Int(Sin(x),x) returns -Cos(x)
- Int(Sin(x),x)/.x->Pi returns 1
Input
- ACos(argument)
- ACos(x)
- ACos(X(A))
Input
- ASin(argument)
- ASin(x)
- ASin(X(A))
Input
- ATan(argument)
- ATan(x)
- ATan(X(A))
Input
- Cos(argument)
- Cos(x)
- Cos(X(A))
input
- Cot(argument)
- Cot(x)
- Cot(X(A))
Input
- Sin(argument)
- Sin(x)
- Sin(X(A))
Input
- Tan(argument)
- Tan(x)
- Tan(X(A))
Input
- Abs(argument)
- Abs(-2) returns 2
- Abs(x) returns -x if x<0, otherwise x
Input
- Max(argument1, ... , argumentN)
- Max(1,2,3) returns 3
- Max(-3,0.4,-5.1) returns 0.4
Input
- Min(argument1, ... , argumentN)
- Min(1,2,3) returns 1
- Min(-3,0.4,-5.1) returns -5.1
Input
- N(argument)
- N(Sqrt(2)) returns 1.414...
- N(E) returns 2.718...
Input
- Round(argument, n)
Examples
- Round(2.234623,2) returns 2.23
- Round(2.234623,3) returns 2.235
- Round(2.234623,0) returns 2.0
- Round(2.2300000,4) returns 2.23
Input
- Sign(argument)
- Sign(-2) returns -1
- Sign(5.56) returns 1
- Sign(x) returns -1 if x<0, 0 if x=0 and 1 if x>0
Input
- Trunc(number)
Examples
- Trunc(3.523453) returns 3.0
- Trunc(-3.4564564) returns -3.0
Input
- argument1 == argument2
Input
- argument1 > argument2
"greater than or equal to"-operator
Input
- argument1 >= argument2
Input
- argument1 < argument2
"lesser than or equal to"-operator
Input
- argument1 <= argument2
Eingabe
- argument1 != argument2
Input
- And(argument1, ... , argumentN)
- argument1 && ... && argumentN
Examples
- And(5>0,3<Pi) returns True
- a && b with a=False and b=True returns False
Input
- Or(argument1, ... , argumentN)
- argument1 || ... || argumentN
Examples
- Or(5>0,3>Pi) returns True
- a || b with a=False and b=True returns True
Input
- If(condition, true, false)
Examples
- If(5>0,5.3,4.0) returns 5.3
- If(5<0,5.3,4.0) returns 4.0
- If(X(A)<0,X(B)=5,X(B)=X(A)) eith X(A)=-2.5 returns X(B)=5
Input
- Pi
Input
- E
Input
- False
Input
- True
See Also:
 Top of Page
Top of Page (x;y)-Punkt
(x;y)-Punkt Angle (input size)
Angle (input size) Circle (input radius)
Circle (input radius) Graph of a function
Graph of a function parameter curve
parameter curve Text
Text